Periods
Every month, millions of women around the world experience a natural bodily process called menstruation, commonly known as periods. Despite being a normal part of a woman's reproductive cycle, periods are often accompanied by a stigma and misconceptions. In this blog, we will delve into the topic of periods, discussing their purpose, the menstrual cycle, common symptoms, and ways to manage them effectively. By shedding light on this natural phenomenon, we hope to contribute to a more informed and open conversation about periods.
What is Menstruation?
The uterine lining sheds each month during menstruation. Menstruation may also be referred to as menses, menstrual period, cycle, or period. Menstrual blood leaves your uterus through your cervix and exits your body through your vagina. Menstrual blood is partially blood and partially tissue from inside your uterus.
Hormones control the onset of menstruation. Your body uses hormones as chemical messengers. At specific moments during your menstrual cycle, your ovaries, a component of your reproductive system, and your pituitary gland, located in your brain, produce and release specific hormones.
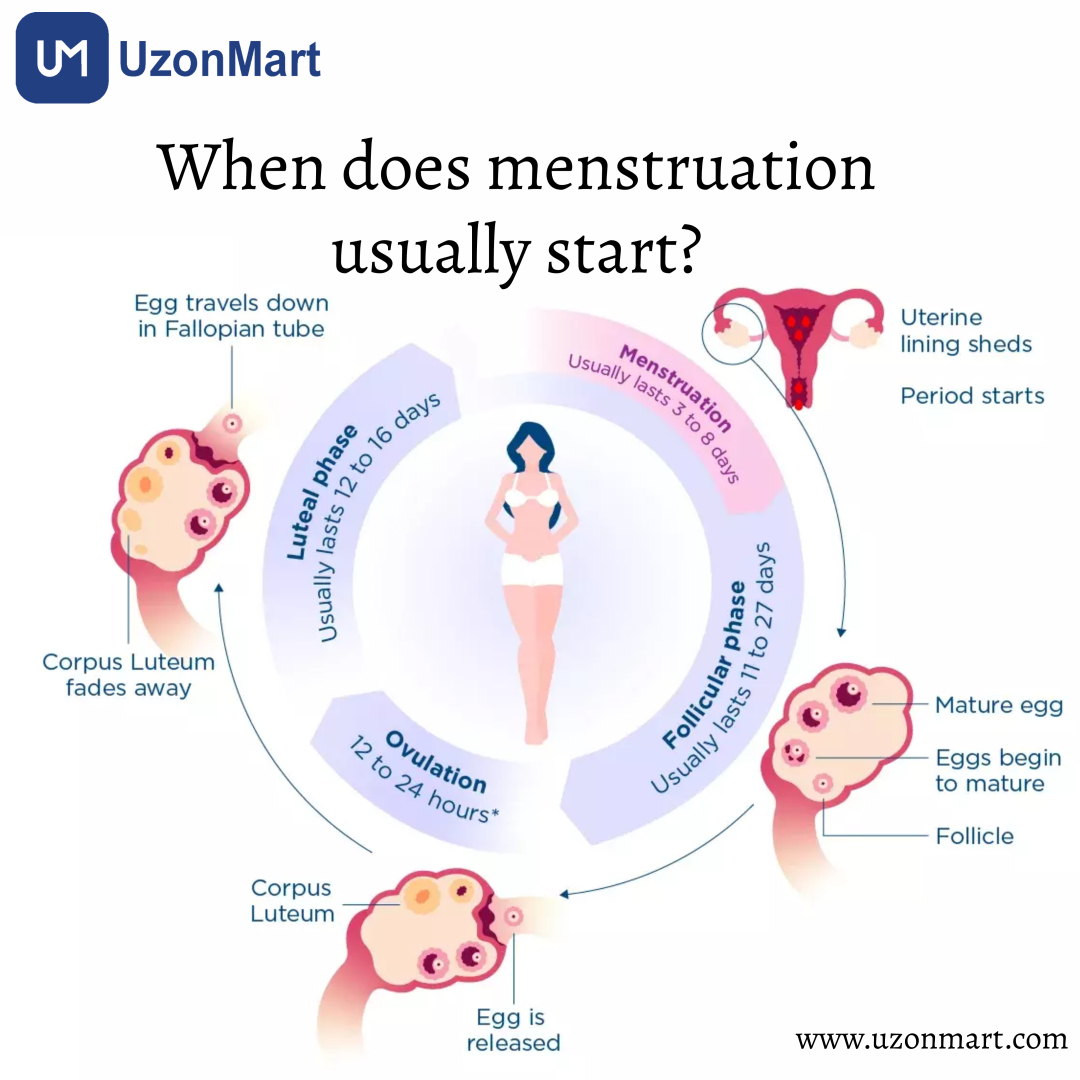
The lining of your uterus becomes thicker as a result of these hormones. This occurs so that an egg can implant into your uterine lining in the event of a pregnancy. Your ovaries release an egg (ovulation) as a result of hormones. The egg travels via your fallopian tubes and waits for sperm there. Pregnancy cannot occur if a sperm does not fertilize that egg. Your uterus' lining degrades and sheds. You are on your menstruation.
How long is a normal Menstrual Cycle?
A normal menstrual cycle typically lasts between 21 to 35 days, although variations outside this range can still be considered normal for some individuals. The length of the menstrual cycle is counted from the first day of one period to the first day of the next period. The average menstrual cycle is around 28 days, but it's important to note that cycles can vary from person to person.
The menstrual cycle is divided into different phases, including the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase. The follicular phase begins on the first day of menstruation and lasts until ovulation, which usually occurs around day 14 in a 28-day cycle. Ovulation is the release of an egg from the ovaries. Following ovulation, the luteal phase begins and lasts until the start of the next menstrual period.
While it's common for menstrual cycles to have some variations in length occasionally, significant or consistent irregularities may be worth discussing with a healthcare provider. Factors such as stress, hormonal imbalances, certain medical conditions, and lifestyle changes can influence the length and regularity of menstrual cycles. Keeping track of your menstrual cycle using a calendar or a smartphone app can help identify any patterns or irregularities over time.
How long does a typical period last?

A typical period, commonly known as menstrual bleeding, lasts between three and seven days. The length, though, may differ from person to person. Some people might have shorter intervals that just last a few days, while others might have lengthier durations that go over a week.
It's vital to remember that monthly bleeding may flow lighter during the first few and last few days than throughout the middle days. Throughout time, the flow may change, becoming heavier or lighter on different days.
When does menstruation usually start?
On average, a person begins her period at the age of 12. However, you can start having periods as early as age 8 or as late as age 16. The majority of people typically start menstruating a few years after developing breasts and pubic hair.
When a woman reaches menopause, which typically happens at age 51, her period stops. You stop ovulating (producing eggs) when you reach menopause. If you haven't had a period in a year, you are in menopause.
Having a menstrual period that lasts for three days is considered normal and falls within the range of what is typically expected. While it may be shorter compared to the average duration, which is usually around 3 to 7 days, a three-day period is still within the normal range and should not raise concerns.
Is a three-day menstruation normal?
Having a menstrual period that lasts for three days is considered normal and falls within the range of what is typically expected. While it may be shorter compared to the average duration, which is usually around 3 to 7 days, a three-day period is still within the normal range and should not raise concerns.
How do you know when your period is coming?
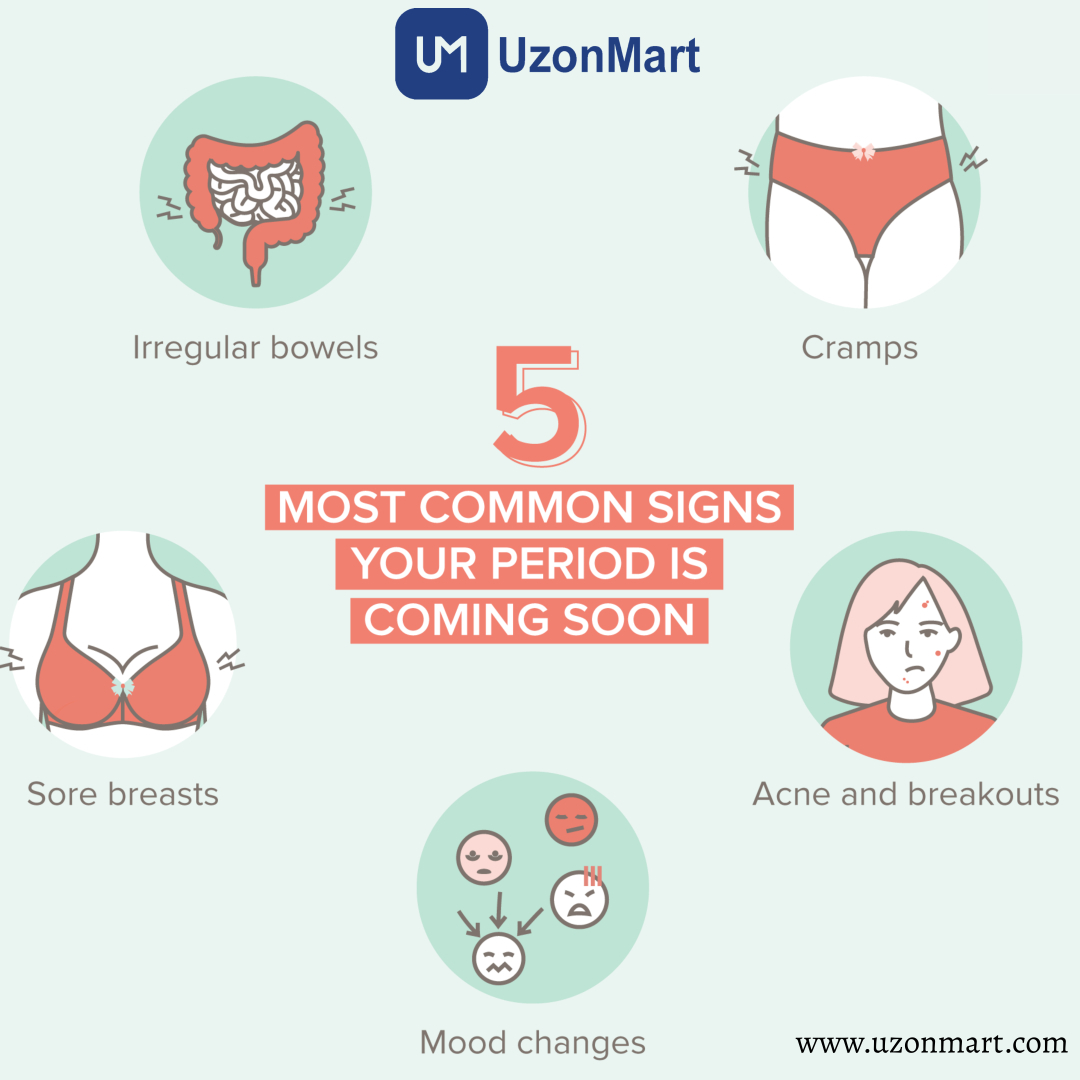
Menstruation, usually known as receiving your period, can cause a variety of symptoms. Each person will experience these symptoms differently, and some people may experience more severe symptoms than others. Here are a few typical signs and symptoms of menstruation:
- Many people have stomach or pelvic cramping before or during their period (dysmenorrhea). Mild to severe cramps can be experienced.
- Mood swings, impatience, or emotional sensitivity can be brought on by hormonal shifts during the menstrual cycle.
- Breast pain or swelling may be experienced by some persons as premenstrual symptoms.
- Bloating: Hormonal shifts can result in water retention and bloating, which can make the belly feel heavy or swollen.
- Fatigue: For some people, feeling exhausted or having low energy levels is a common symptom.
- Headaches: Some people get headaches or migraines during their period due to hormonal changes.
- Changes in the skin, such as outbreaks of acne or alterations in the texture, may be noticed by some people.
- Food cravings or changes in appetite: During the menstrual cycle, some foods may cause cravings or changes in appetite.
The severity and duration of these symptoms can differ from person to person, despite the fact that they are generally present. You should seek medical advice from a professional for further assessment and direction if you feel excruciating pain, unusually heavy bleeding, or any other unsettling symptoms that severely affect your day-to-day activities.
How has the cycle of your period changed over time?

From your teenage years through your 40s or 50s, your menstrual cycle can fluctuate. It's typical to have longer cycles or a greater period flow when you initially start your period. After starting to menstruate, it might take young people up to three years to have regular cycles. A typical menstrual cycle includes the following:
- occurs every 21 to 35 days on average.
- brings on bleeding for three to seven days.
Your menstrual cycles grow more regular and reliable as you get older. Your cycles will shift once again and become more erratic as your body enters menopause.
How can my menstrual cycle be tracked?
Tracking your menstrual cycle can be helpful for understanding its patterns and predicting when your next period is due. Here are some methods you can use to track your menstrual cycle:
Calendar method: Mark the first day of your period on a calendar and count the number of days until the next period starts. This can give you an estimate of the length of your cycle. Over time, you may notice a pattern emerging.
Smartphone apps: There are various smartphone apps available specifically designed for menstrual cycle tracking. These apps allow you to input the start and end dates of your periods, track symptoms, record mood changes, and provide predictions for future cycles. Popular examples include Clue, Flo, and Period Tracker.
Menstrual cycle tracking devices: There are wearable devices and smartwatches available that can track your menstrual cycle by monitoring various physiological indicators, such as body temperature, heart rate, and movement. These devices often come with associated apps that provide insights and predictions.
Paper or online trackers: You can also use a physical paper tracker or an online tracker where you manually record the start and end dates of your periods. Many websites offer printable menstrual cycle tracking sheets that you can fill out.
When tracking your menstrual cycle, it's helpful to note any accompanying symptoms or changes you experience, such as cramps, mood swings, or changes in cervical mucus. This additional information can provide a more comprehensive picture of your menstrual health.
By consistently tracking your menstrual cycle over several months, you can identify patterns, understand the length of your cycle, and predict when your next period is likely to occur. This knowledge can help you plan ahead and manage your menstrual health more effectively.
What leads to irregular menstrual cycles?
Menstrual cycle irregularities can be caused by various factors, including:
Hormonal imbalances: Fluctuations in estrogen, progesterone, and other hormones can disrupt the regularity of the menstrual cycle. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, and hormonal changes during perimenopause can contribute to hormonal imbalances.
Stress: High levels of physical or emotional stress can impact hormone production and interfere with the normal menstrual cycle.
Weight changes: Significant weight loss, weight gain, or fluctuations in body weight can disrupt hormone levels and affect the regularity of periods.
Medications and contraceptives: Certain medications, including hormonal contraceptives, can alter menstrual bleeding patterns. Starting or stopping hormonal birth control methods may cause temporary irregularities.
Chronic health conditions: Conditions such as PCOS, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, and pelvic inflammatory disease can lead to menstrual irregularities.
Menopause and perimenopause: As women approach menopause, their hormone levels naturally fluctuate, leading to irregular periods. Perimenopause refers to the transitional phase leading up to menopause and is often associated with menstrual irregularities.
Lifestyle factors: Factors like excessive exercise, travel, disrupted sleep patterns, smoking, and excessive alcohol or caffeine consumption can contribute to menstrual cycle irregularities.
It's important to remember that occasional variations in the menstrual cycle are normal, but if you experience persistent or significant irregularities, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider. They can help determine the underlying cause and provide appropriate guidance or treatment.
What types of products are there for period management?

There are several different period management products available to help individuals manage their menstrual flow. Here are some commonly used options:
- Menstrual pads
- Tampons
- Menstrual cups
- Period underwear
- Menstrual discs
- Menstrual sponges
It's important to choose a period management product that suits your comfort, lifestyle, and menstrual flow. You may need to try different options to find what works best for you. Additionally, maintaining proper hygiene by changing products regularly and following the manufacturer's instructions is essential for menstrual health.
Conclusion
A critical first step in empowering women and promoting an inclusive society is to understand menstruation. We may foster an environment where menstruation is viewed as a typical and natural aspect of a woman's life by shattering the taboo and eliminating falsehoods. Let's keep educating ourselves and others, offering support and working to make the world a place where menstruation is treated with respect, compassion, and understanding.
UzonMart values your opinions, and we go above and beyond to ensure you have a trouble-free experience. By leaving a review on our website, you can both inform others how to make better decisions and let us know how we're doing. We appreciate you choosing UzonMart.