Depression
Millions of individuals all over the world are afflicted by the widespread mental health disease known as depression. Despite its prevalence, it remains one of the most misunderstood and stigmatized disorders. Often referred to as the "silent struggle," depression can have a profound impact on an individual's life, relationships, and overall well-being.
In this blog, we will delve into the intricacies of depression, exploring its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options. By raising awareness and fostering empathy, we hope to create a more compassionate society for those grappling with depression.
What is Depression?
Depression is a mood disease characterized by persistent feelings of melancholy and a lack of interest in or enjoyment of activities. It is sometimes referred to as clinical depression or major depressive disorder. It may affect people's ideas, feelings, and behaviors on a range of levels and across various ages, genders, and ethnicities. A person's ability to function in daily life, maintain relationships, and enjoy an acceptable level of living might occasionally be hindered by depression's mental and physical side effects. It is vital to understand that depression is not a sign of weakness and that one cannot simply will themselves to "snap out" of it.
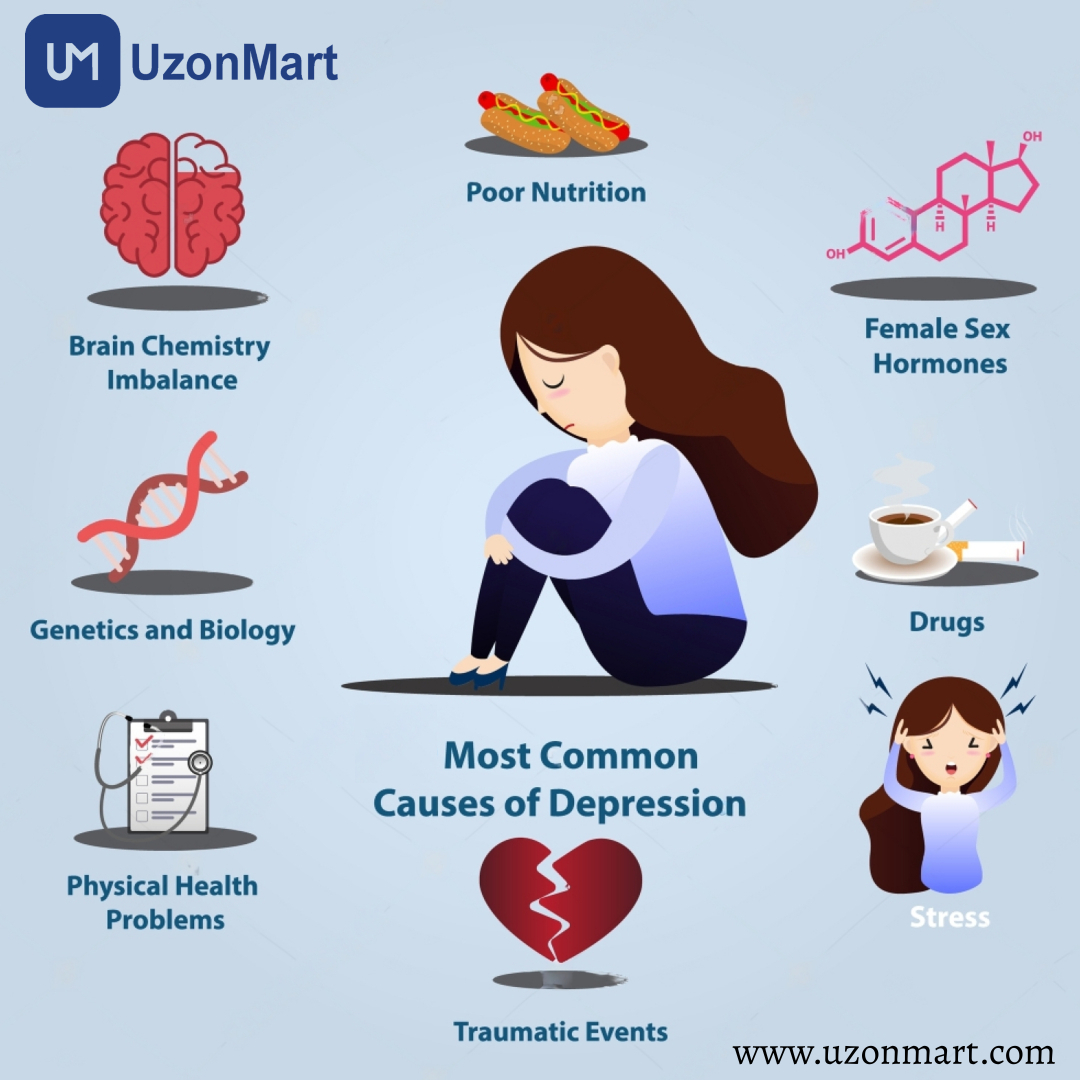
Causes of Depression
There are many different variables that might contribute to depression, including biological, genetic, environmental, and psychological ones. While the exact cause of depression is not fully understood, here are some factors that are believed to contribute to the development of depression:
Biological Factors: Imbalances in certain chemicals in the brain, such as neurotransmitters like serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, are thought to play a role in depression. Changes in the functioning of the limbic system, which is involved in emotional regulation, may also contribute to depressive symptoms.
Genetics: Families with a history of depression may be predisposed to it genetically. Having a family history of depression or other mood disorders increases the likelihood of developing depression.
Environmental Factors: Stressful life events, such as the loss of a loved one, relationship problems, financial difficulties, or major life changes, can trigger or contribute to depression. Traumatic experiences, abuse, neglect, or chronic stress can also increase the risk.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as chronic illnesses, hormonal imbalances (e.g., thyroid disorders), neurological conditions, or chronic pain, can be associated with an increased risk of developing depression.
Medications and Substance Abuse: Some medications, such as certain types of steroids or beta-blockers, can be linked to depressive symptoms. Substance abuse, including alcohol or drug misuse, can also contribute to or worsen depression.
Personality and psychological factors: People may be more susceptible to depression if they have certain personality qualities including low self-esteem, pessimism, perfectionism, or a history of childhood trauma. Coexisting mental health conditions, such as anxiety or eating disorders, can also be risk factors.
It's important to note that these factors do not directly cause depression in every individual. They interact in complex ways, and the development of depression is often influenced by a combination of multiple factors. Treatment for depression typically involves a holistic approach that addresses these various factors to provide relief and support to individuals experiencing depression.
Symptoms of Depression
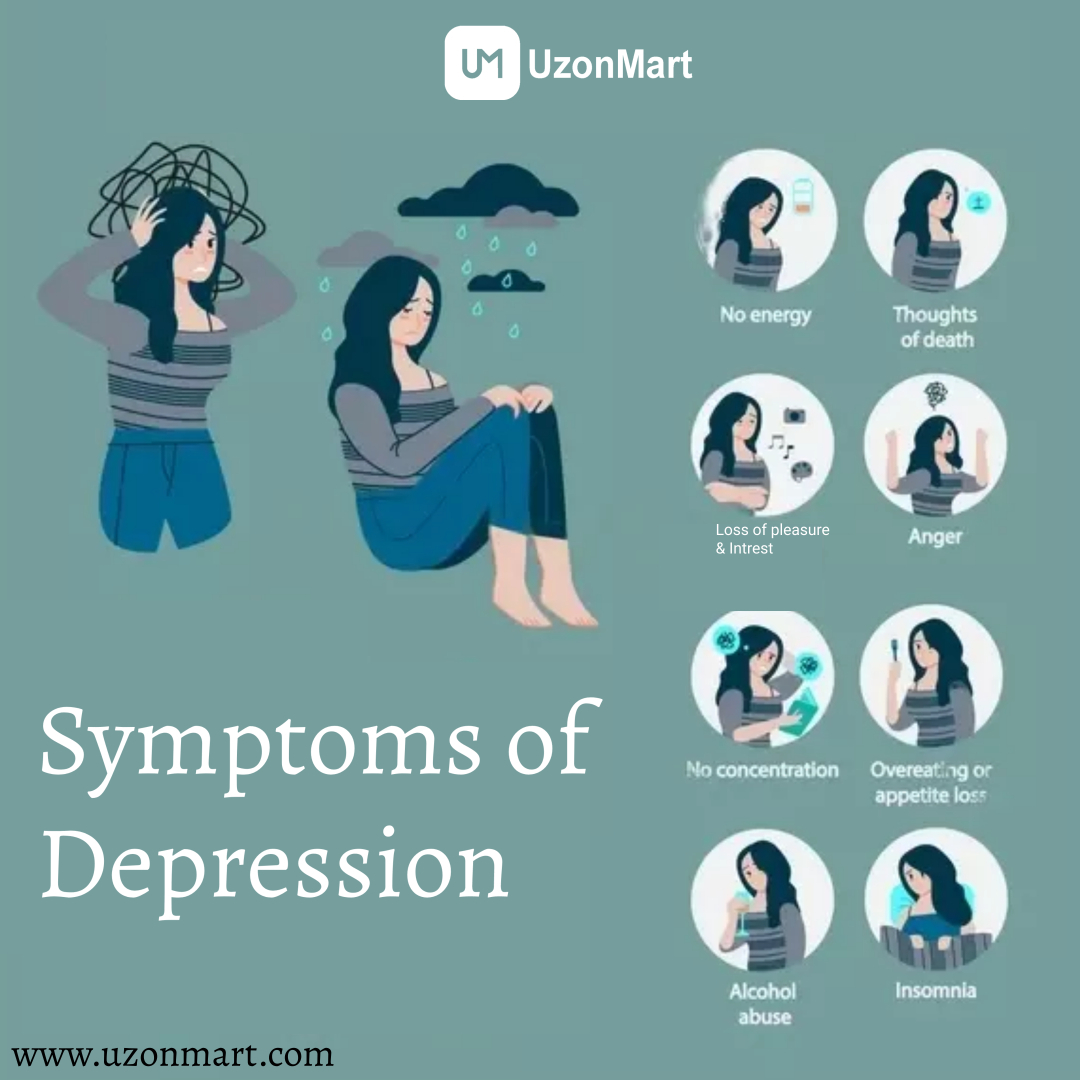
Symptoms of depression can vary among individuals, and the severity and duration of these symptoms can differ. It's important to note that experiencing a few of these symptoms does not necessarily indicate clinical depression. However, if you or someone you know consistently experiences several of these symptoms, and they significantly interfere with daily functioning, it is advisable to seek professional help. Depression is more than just a constant state of sadness or feeling "blue." It can manifest with a range of symptoms that affect both mood and the body. These symptoms can be persistent or fluctuate over time.
Here are some common symptoms of depression:
- Persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or emptiness.
- Loss of enjoyment or interest in once-enjoyed activities.
- Weight changes that are significant, either weight gain or decrease.
- Difficulty sleeping, such as insomnia or excessive sleeping.
- Fatigue or loss of energy, feeling constantly tired.
- Feelings of worthlessness or excessive guilt.
- Difficulty concentrating, making decisions, or remembering things.
- Restlessness or irritability.
- Withdrawal from social activities, avoiding friends or family.
- Suicidal ideas, attempts, or persistent death thoughts.
The signs of depression might manifest differently in men, women, teenagers, and young kids.
Males may experience signs connected to:
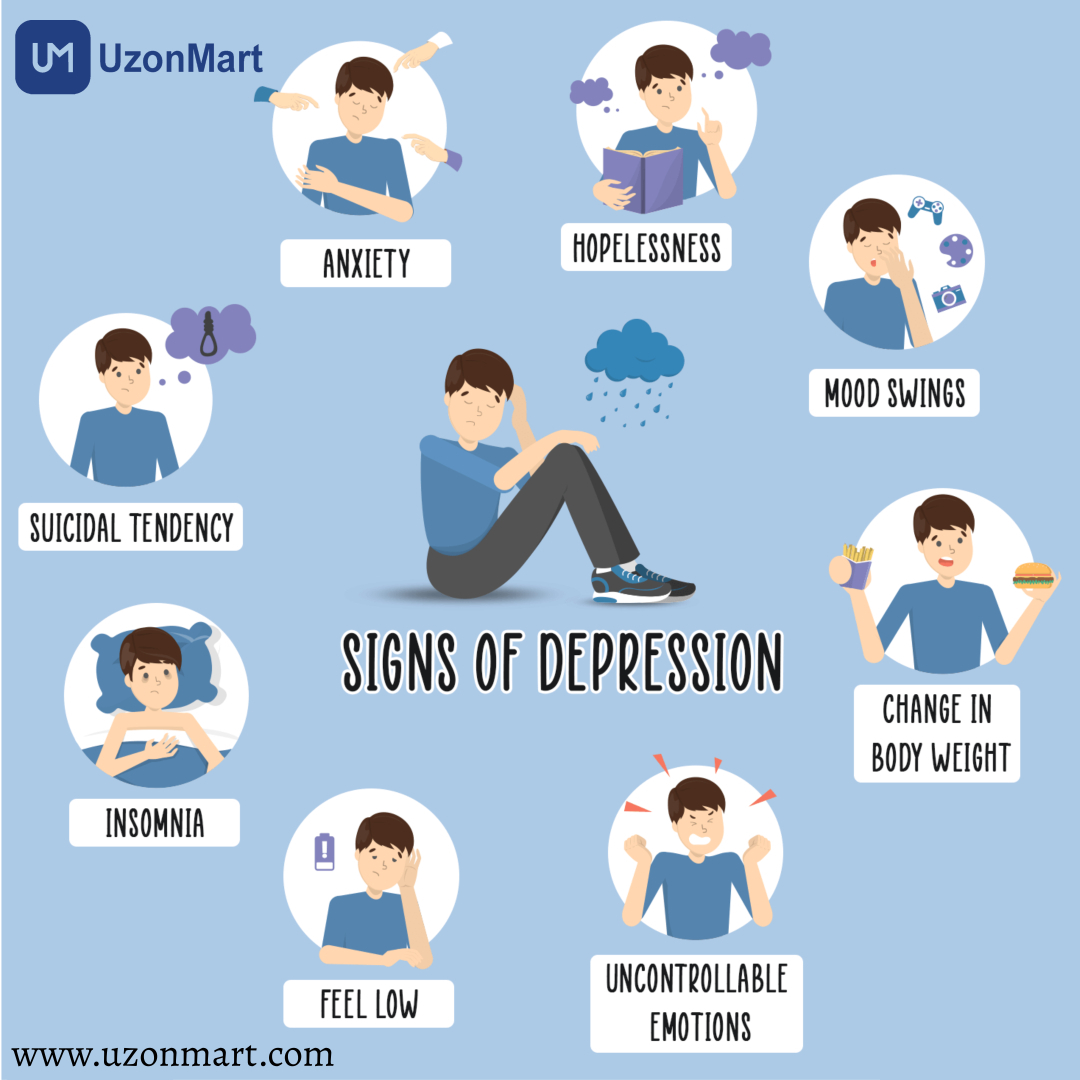
- Emotions such as rage, aggression, impatience, fear, or restlessness.
- Mental well-being, such as feeling exhausted, downhearted, or despairing.
- Conduct, such as disinterest, lack of enjoyment in previously enjoyed hobbies, feeling fatigued quickly, suicidal thoughts,
- Excessive drinking, drug use, or participation in high-risk activities.
- Lack of interest in sexual activity, such as a lack of lust or diminished sexual drive.
- Cognitive skills, including problems focusing, difficulties finishing activities, or slow response times in dialogues.
- Sleep habits, such as insomnia, restless sleep, being too tired, or not sleeping through the night.
- Physical health, such as exhaustion, aches, headaches, or stomach issues.
The following symptoms may be present in Females:
- Mental state, such as agitation
- Emotional health, including emotions like sadness or emptiness, anxiety, or hopelessness
- Conduct, such as apathy towards activities, retreat from social interactions, or suicidal thoughts
- Cognitive skills, such as the ability to think or speak more slowly
- Physical health, including decreased energy, increased tiredness, changes in appetite, weight changes, aches, pains, headaches, or a rise in cramps.
- Sleep patterns, such as difficulties sleeping through the night, getting up early, or sleeping too much.
Children can also exhibit symptoms related to depression:

- Moods, such as agitation, rage, mood swings, or tears.
- Emotional health, including dejection, sobbing, or extreme unhappiness; feelings of incapacity (e.g., "I can't do anything right"); or both.
- Actions such as getting into problems at school or not wanting to go to school, avoiding friends or siblings, having suicide or death. thoughts, or harming oneself.
- Cognitive skills, including issues with concentration, a drop in academic achievement, or changes in grades.
- Irregular sleep patterns, such as trouble falling asleep or oversleeping.
- Physical health, including fatigue, gastrointestinal issues, changes in appetite, and weight gain or loss.
It's crucial to keep in mind that each person's experience with depression is different, and not everyone will exhibit the same set of symptoms. A combination of symptoms that affect the body, mind, and emotions is also conceivable. Reaching out to a medical expert or mental health practitioner for an assessment and the necessary help is imperative if you or someone you know is exhibiting these symptoms.
Types of Depression
There are different types of depression that can vary in their symptoms, duration, and underlying causes. Here are some common types of depression:
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD): Also known as clinical depression, it is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest or pleasure in activities. Typically, symptoms last for at least two weeks and last for the majority of the day almost every day.
Persistent Depressive Disorder (PDD): Formerly known as dysthymia, this type of depression involves chronic depressive symptoms that last for at least two years. Symptoms may be less severe compared to MDD but can be long-lasting and affect daily functioning.
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD): SAD is a type of depression that occurs seasonally, typically during the fall and winter months when there is less sunlight. Symptoms may include low mood, increased sleep, weight gain, and a lack of energy. It tends to resolve with the onset of spring.
Postpartum Depression (PPD): PPD occurs in individuals after childbirth. It involves feelings of extreme sadness, anxiety, and exhaustion that can interfere with the ability to care for oneself and the baby. PPD can develop within weeks to months after delivery.
Psychotic Depression: This form of depression is accompanied by psychotic symptoms, such as hallucinations or delusions. Individuals may experience false beliefs or perceive things that are not real, often related to themes of guilt, poverty, or illness.
Bipolar Disorder: Although bipolar disorder is mostly a mood disease marked by episodes of both mania (elevated mood and enhanced activity) and depression, bipolar disorder's depressive episodes can resemble symptoms of major depressive disorder. Manic or hypomanic bouts alternate with depressive episodes.
It's important to note that these types of depression are not mutually exclusive, and individuals may experience a combination or variation of symptoms. Proper diagnosis and evaluation by a healthcare professional or mental health provider are essential in determining the specific type of depression and guiding appropriate treatment.
How to Overcome Depression?
Overcoming depression is a complex process that may require a combination of strategies and professional help. Here are some steps that can be helpful:
Seek Professional Help: Start by reaching out to a healthcare professional or mental health provider. They can provide an accurate diagnosis, evaluate the severity of your depression, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Follow a Treatment Plan: Work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that may include therapy, medication, or a combination of both. Adhering to the prescribed treatment plan is crucial for managing and overcoming depression.
Engage in Therapy: Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be highly effective in treating depression. It helps identify negative thought patterns and behaviors, develop coping skills, and promote positive changes in thinking and behavior.
Build a Support System: Create a Support System by surrounding yourself with sympathetic and perceptive people. Inform close family or friends who can assist you emotionally with your feelings. Consider joining support groups where you can connect with others who have experienced similar challenges.
Practice Self-Care: Take care of your physical and emotional well-being by engaging in self-care. Engage in regular exercise, maintain a healthy diet, prioritize sleep, and practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or mindfulness. Self-care activities that bring you joy and fulfillment can also help improve your mood.
Challenge Negative Thoughts: Negative thinking patterns often accompany depression. Learn to identify and challenge negative thoughts by replacing them with more positive and realistic ones. In this aspect, CBT techniques can be quite beneficial.
Set Realistic Goals: Break down tasks into smaller, manageable steps and set achievable goals. Celebrate even small victories, as they contribute to a sense of accomplishment and progress.
Maintain Routine and Structure: Establishing a daily routine can provide stability and a sense of purpose. Make an effort to engage in activities you enjoy, even if you don't feel motivated initially.
Avoid Isolation: Stay socially connected. Engage in activities that involve interaction with others, such as joining clubs or organizations, volunteering, or participating in community events.
Reach out for Support: Don't be hesitant to call a helpline, crisis hotline, or emergency services right away if you are experiencing suicidal thoughts or are having problems coping.
Keep in mind that getting over sadness requires patience and time. It's critical to be fair to yourself and accept that change may occur in baby steps. It is possible to control and get over depression with the correct assistance and care.
Conclusion
A person's life can be greatly impacted by depression, a serious mental health disorder. Steps towards recovery include comprehending the nature of depression, recognizing the symptoms, getting professional assistance, and implementing coping mechanisms. Keep in mind that you are not traveling alone. Reach out, ask for assistance, and have faith that healing is possible. It is possible to recover from depression and find joy and fulfillment in life with the correct assistance and care.
UzonMart loves your feedback, and we go above and beyond to make sure you don't run into any problems. You may help others make better selections and let us know how we're doing by writing a review on our website. We are grateful that you choose UzonMart.